Treatment for Benign Lung Tumor: Comprehensive Guide
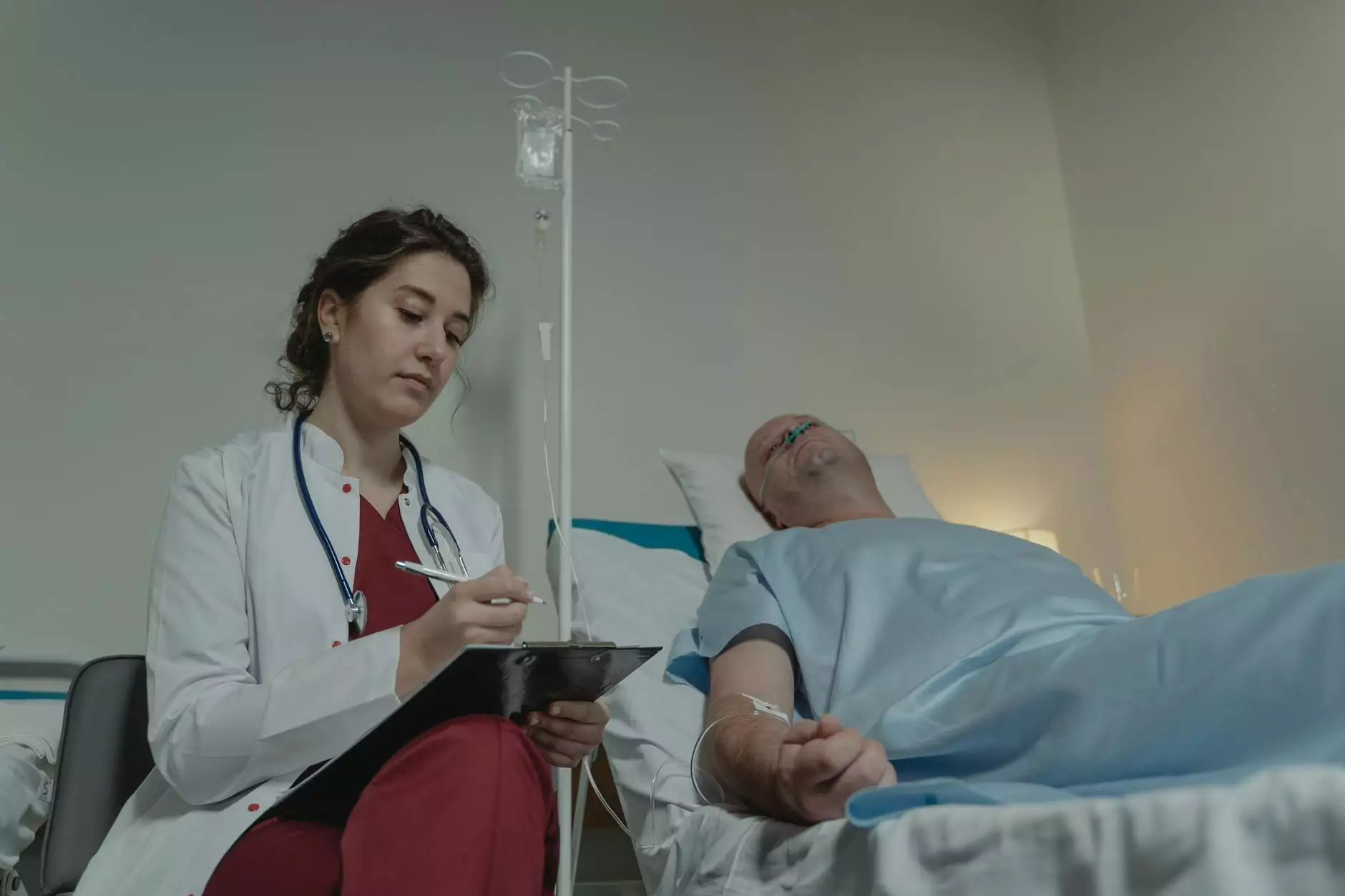

Benign lung tumors are non-cancerous growths that can occur in the lungs, often leading to symptoms that may mimic those of malignant tumors. Although they are typically not life-threatening, it is crucial to understand their nature, the types that exist, and the best treatment options available to manage them effectively. This article explores everything you need to know about benign lung tumors and their treatment, with a focus on insights from Neumark Surgery.
What are Benign Lung Tumors?
Benign lung tumors, unlike their malignant counterparts, do not spread to other parts of the body and are usually encapsulated. These tumors can occur in various forms, including:
- Hamartomas: These are the most common benign tumors found in the lung, made up of a mix of tissues normally found in lung tissue.
- Granulomas: Often resulting from infections or inflammation, these are collections of immune cells that form in response to irritants.
- Adenomas: These tumors originate from glandular tissue and can occur in the lungs.
- Neurogenic tumors: Arising from the nerves within the lungs, these are less common but are still classified as benign.
Symptoms of Benign Lung Tumors
In many cases, benign lung tumors do not produce symptoms and may be discovered incidentally during imaging studies for other health issues. However, when symptoms do manifest, they can include:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Repeated respiratory infections
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen, it is essential to seek medical advice from a qualified healthcare provider.
Diagnosis of Benign Lung Tumors
Diagnosing a benign lung tumor typically involves a range of imaging and diagnostic tests to evaluate the presence, size, and characteristics of the tumor:
- Chest X-ray: A standard imaging technique that can help identify abnormal masses in the lungs.
- CT Scan: Provides more detailed images of the lungs and can help distinguish between benign and malignant lesions.
- MRI: Useful in specific cases to further evaluate lung tumors and their characteristics.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a tissue sample may be necessary to conclusively determine the nature of the tumor.
Treatment Options for Benign Lung Tumors
The treatment for benign lung tumors often depends on various factors, including the tumor's size, location, and whether it is causing symptoms. Here are the primary treatment options:
1. Observation and Monitoring
For many individuals, especially if the tumor is asymptomatic and small, a "watch and wait" approach may be recommended. Regular follow-up with imaging studies ensures that the tumor remains stable and does not develop into a more significant issue.
2. Surgical Intervention
If a benign lung tumor causes symptoms or significant respiratory issues, or if it grows over time, surgical intervention may be necessary. The most common surgical options include:
- Lobectomy: Removal of the lobe of the lung where the tumor is located; this is common in cases where the tumor is large or symptomatic.
- Wedge Resection: Involves removing a small, wedge-shaped portion of lung tissue containing the tumor, preserving more lung than a lobectomy.
- Pneumonectomy: In rare cases where the tumor is extensive, the entire lung may be removed.
3. Other Treatment Methods
Depending on the individual case, other treatments may be appropriate:
- Endobronchial resection: A less invasive approach that can remove tumors located in the bronchi using bronchoscopy techniques.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This minimally invasive technique uses heat to destroy tumor cells and may be suitable for certain patients, especially for those who are not candidates for surgery.
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery
Recovery after treatment for a benign lung tumor varies based on the method of treatment, but may include:
- Follow-up imaging: Regular monitoring with X-rays or CT scans to ensure no recurrence.
- Lung function tests: To assess how well the lungs are functioning after surgery.
- Rehabilitation exercises: These are vital to restore lung capacity and strength, especially after surgical interventions.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of treatment for benign lung tumors allows patients to make informed decisions in partnership with their healthcare providers. At Neumark Surgery, specialists are dedicated to providing comprehensive care for individuals affected by these conditions. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans are essential for optimal outcomes.
If you suspect that you might have a benign lung tumor or are experiencing any related symptoms, it is vital to schedule an appointment with a qualified medical professional who can guide you through the diagnostic process and discuss potential treatment options. Your health is paramount, and understanding your condition empowers you to take the necessary steps towards recovery and wellbeing.