Understanding Myofascial Pain Syndrome of Thoracic Spine
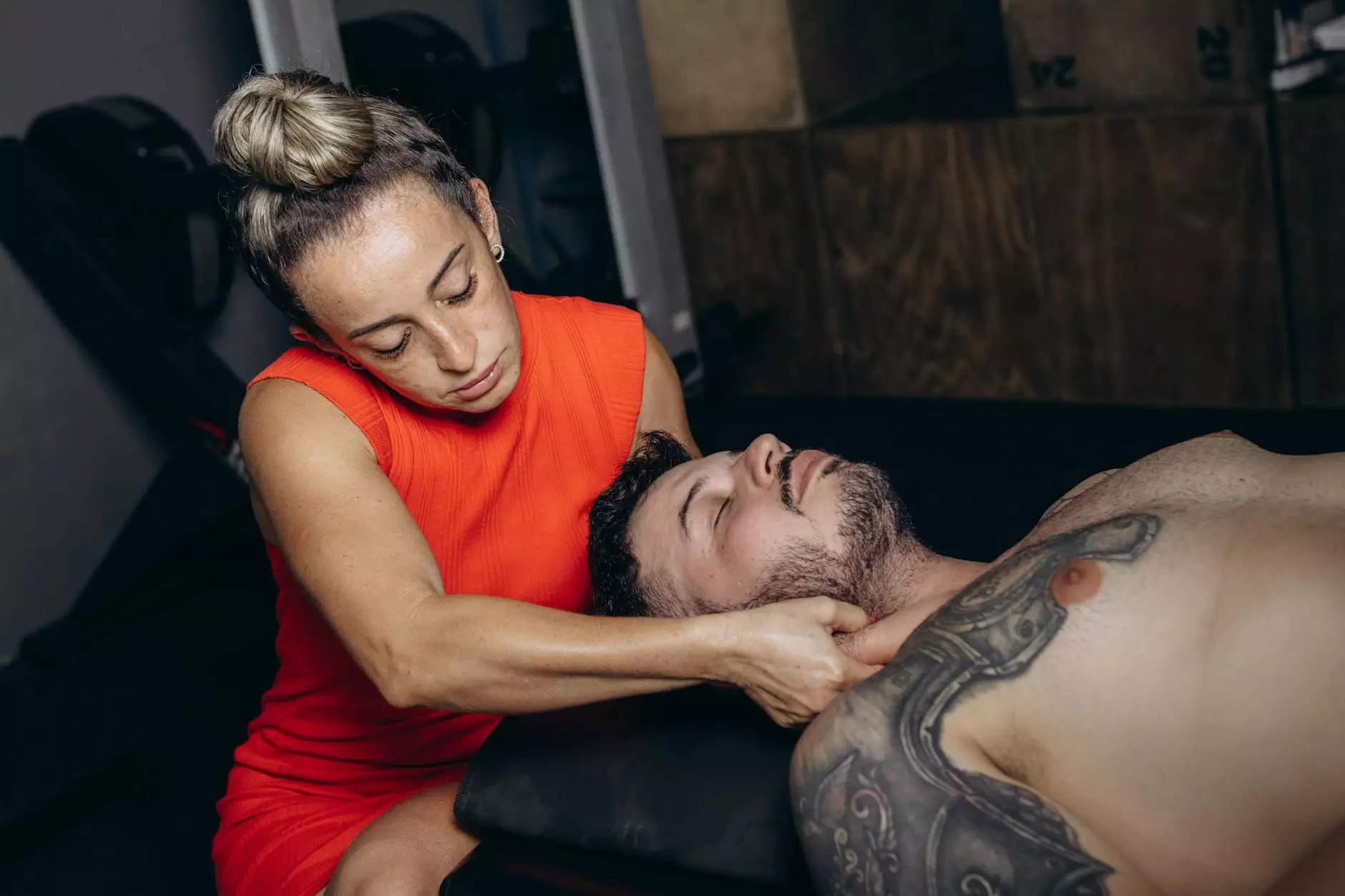

Myofascial pain syndrome of thoracic spine is a complex disorder that affects many individuals, often leading to chronic discomfort and restricted mobility. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of this syndrome, examining its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. Our goal is to provide valuable insights that will help you better understand this condition and how it can be managed effectively.
What is Myofascial Pain Syndrome?
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is characterized by the presence of trigger points in the fascia, which is the connective tissue that surrounds muscles. These trigger points can lead to referred pain, discomfort, and muscle tightness. When MPS affects the thoracic spine, it can result in significant limitations in daily activities.
Understanding the Thoracic Spine
The thoracic spine is the middle portion of the vertebral column, consisting of twelve vertebrae (T1-T12). This region plays a critical role in supporting the ribcage and protecting the organs within the thorax. Due to its structural composition and the loads it bears, the thoracic spine is susceptible to various forms of strain and injury, including myofascial pain syndrome.
Causes of Myofascial Pain Syndrome of Thoracic Spine
Several factors can contribute to the development of myofascial pain syndrome in the thoracic spine:
- Muscle Overuse: Repetitive movements can lead to muscle fatigue and irritation, resulting in trigger points.
- Postural Issues: Poor posture, especially during prolonged periods of sitting or standing, can strain the muscles of the thoracic spine.
- Injuries: Trauma from accidents or falls can initiate the onset of myofascial pain.
- Stress: Emotional stress can lead to muscle tension, exacerbating pain symptoms.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can weaken muscles, making them more prone to injury.
Identifying Symptoms of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
The symptoms of myofascial pain syndrome of thoracic spine can vary among individuals, but here are some common signs to be aware of:
- Localized Pain: The pain is often localized to specific areas of the thoracic spine and may radiate to other regions, such as the shoulders and arms.
- Muscle Stiffness: Affected individuals may experience stiffness that limits their range of motion.
- Trigger Points: Palpable knots or tight areas can often be felt in the muscle tissue.
- Fatigue: Chronic pain can lead to physical and mental fatigue, impacting overall quality of life.
- Tenderness: Areas of the thoracic spine may be tender to the touch, making any movement uncomfortable.
Diagnosis of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Diagnosing myofascial pain syndrome primarily involves a comprehensive physical examination, along with a review of the patient’s medical history. Health professionals, especially chiropractors and physiotherapists, are skilled in identifying trigger points and assessing movement limitations. Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays or MRIs, may also be utilized to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Treatment for myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine focuses on alleviating symptoms and addressing the underlying causes. Here are several effective approaches:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is crucial in managing myofascial pain syndrome. Therapists use various techniques, such as:
- Stretching Exercises: To alleviate tightness and improve flexibility.
- Strengthening Exercises: To support the muscles around the thoracic spine and improve posture.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques to release trigger points and improve muscle function.
2. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors specialize in spinal alignment and can offer treatment options such as:
- Spinal Manipulation: Adjustments to reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Myofascial Release: Gentle pressure applied to the fascia to reduce tension and restore movement.
3. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can be effective in managing symptoms. In some cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe:
- Muscle Relaxants: To relieve muscle spasms.
- Antidepressants: Certain types can help manage chronic pain.
4. Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief through alternative treatments, which include:
- Acupuncture: Can help in reducing pain and promoting relaxation.
- Massage Therapy: Effectively addresses muscle tension and promotes overall well-being.
5. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact the management of myofascial pain syndrome:
- Posture Correction: Utilizing ergonomic furniture and being mindful of posture can reduce strain on the thoracic spine.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities like yoga or swimming can enhance flexibility and strength.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing can mitigate stress and decrease muscle tension.
The Role of Education in Treatment and Prevention
Education is fundamental for individuals suffering from myofascial pain syndrome of thoracic spine. Understanding the condition empowers patients to take control of their treatment. Knowledge about trigger points, proper ergonomics, and effective exercises can drastically improve recovery and prevent future episodes.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help
If you suspect you may be suffering from myofascial pain syndrome, it is imperative to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent the condition from progressing and significantly improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
In summary, myofascial pain syndrome of the thoracic spine is a common yet often misunderstood condition. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding its causes, and exploring a variety of treatment options, individuals can effectively manage their pain and enhance their well-being. Whether through physical therapy, chiropractic care, or lifestyle changes, the path to recovery is attainable.
For more information about myofascial pain syndrome and available treatment options, visit IAOM-US, where healthcare professionals are dedicated to providing education and support.